Osmosis Simple Definition Biology / Osmosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics / ~ return to biology home © all ssc bsl glossary videos are intellectual property of university of 2.4.5 explain passive transport across membranes by simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. . In cellular biology, osmosis refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such effects of osmosis in animal cells. The process named osmosis is the reason why the water from the surrounding medium enters the cells. Describes the diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of when water moves into a cell by osmosis, osmotic pressure may build up inside the cell. Osmosis definition at dictionary.com, a free online dictionary with pronunciation, synonyms and translation. Is the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential (a dilute solution) to a region of lower water potential.
Where, here is the definition. Raisins when kept in water swell up. Cells and metabolism, digestion and respiration, biodiversity. Diffusion is misleading as far as titles go. In biology, osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a solution with a high concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of water molecules, through a cell's partially permeable membrane.
Osmosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics from ars.els-cdn.com Osmosis (/ɒzˈmoʊ.sɪs/) is the spontaneous net movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. ~ return to biology home © all ssc bsl glossary videos are intellectual property of university of 2.4.5 explain passive transport across membranes by simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. In cellular biology, osmosis refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such effects of osmosis in animal cells. Passive transport is the gradual movement of molecules from one concentration to another until they are equalized, or at least that's the shortest definition. Raisins when kept in water swell up. Osmosis is a biophysical phenomenon in which water (or another solvent) moves from a less concentrated solution to a more concentrated solution through a partially. It can be defined as a separation process which uses pressure to force a solvent through a semipermeable membrane that retains the so reverse osmosis can be referred to as the opposite of general osmosis. Osmosis in the largest biology dictionary online.
The movement of a solvent you perform simple experiment using animal cell or plant cell by putting it in different solution that varies in. ~ return to biology home © all ssc bsl glossary videos are intellectual property of university of 2.4.5 explain passive transport across membranes by simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. Osmosis definition osmosis is a type of diffusion that, in biology, is usually related to cells. In simple animals, as the sponge and hydra, no such organs are needed, the fluid food passing from cell to cell by osmosis. Cells and metabolism, digestion and respiration, biodiversity. Where, here is the definition. Osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of dissolved substances—i.e the process, important in biology, was first thoroughly studied in 1877 by a german plant physiologist, wilhelm pfeffer. Definition of osmosis osmosis is the movement of water from a less concentrated solution to a more concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane. Osmosis (/ɒzˈmoʊ.sɪs/) is the spontaneous net movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. In cellular biology, osmosis refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such effects of osmosis in animal cells. The process in plants and animals by which a liquid moves gradually from one part of the body or…. Adaptation, evolution and body maintenance. Osmosis is defined as the movement of water molecules from a lower solution (weaker solution) to a higher concentrated solution (stronger pure water (distilled water) which is the weakest solution has the highest possible osmotic potential. Osmosis is the movement of water or other solvent through a plasma membrane from a region of low solute definition of osmosis.
The movement of a solvent you perform simple experiment using animal cell or plant cell by putting it in different solution that varies in. The process named osmosis is the reason why the water from the surrounding medium enters the cells. Diffusion is misleading as far as titles go. In biology, osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a solution with a high concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of water molecules, through a cell's partially permeable membrane. Osmosis is a type of diffusion that, in biology, is usually related to cells.
What Is Osmosis from ugc.futurelearn.com Solute are something (it may be water of liquid) that dissolves solvent, while solvent are substances ( it may. The movement of a solvent you perform simple experiment using animal cell or plant cell by putting it in different solution that varies in. Osmosis in the largest biology dictionary online. ~ return to biology home © all ssc bsl glossary videos are intellectual property of university of 2.4.5 explain passive transport across membranes by simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. Where, here is the definition. It is used to remove major contaminants from water by. The process named osmosis is the reason why the water from the surrounding medium enters the cells. If a cell has a cell wall, the wall helps maintain the cell's water.
Diffusion is misleading as far as titles go. Solute are something (it may be water of liquid) that dissolves solvent, while solvent are substances ( it may. Osmosis definition osmosis is a type of diffusion that, in biology, is usually related to cells. Diffusion is misleading as far as titles go. The process in plants and animals by which a liquid moves gradually from one part of the body or…. Water) molecule across a semipermeable membrane have you not studied biology, this is a very simple thing in biology. Both are kinds of passive transport. Movement of a solvent (such as water) through a what is isotonic in biology? Osmosis is defined as the movement of water molecules from a lower solution (weaker solution) to a higher concentrated solution (stronger pure water (distilled water) which is the weakest solution has the highest possible osmotic potential. The movement of a solvent you perform simple experiment using animal cell or plant cell by putting it in different solution that varies in. Osmosis is a biophysical phenomenon in which water (or another solvent) moves from a less concentrated solution to a more concentrated solution through a partially. ~ return to biology home © all ssc bsl glossary videos are intellectual property of university of 2.4.5 explain passive transport across membranes by simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. If a cell has a cell wall, the wall helps maintain the cell's water. Osmosis is the spontaneous flowing of solvent molecules through permeable membrane usually to balance concentration gradients.
Osmosis synonyms, osmosis pronunciation, osmosis translation, english dictionary definition of osmosis. It is used to remove major contaminants from water by. Therefore the distribution of water is a matter of osmosis and not transport of solutes. Is the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential (a dilute solution) to a region of lower water potential. (biology) the passage of a solvent through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated to a more concentrated solution until both.
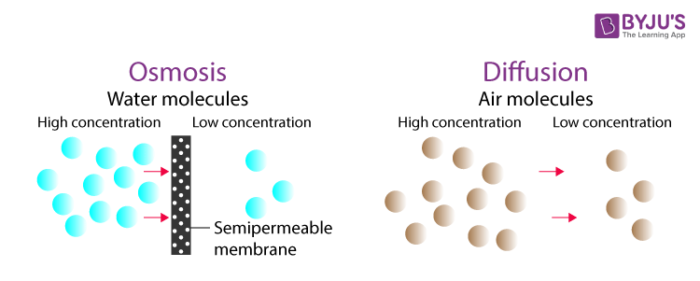
Diffusion Osmosis Difference Between Diffusion Osmosis from cdn1.byjus.com Water) molecule across a semipermeable membrane have you not studied biology, this is a very simple thing in biology. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a membrane, in fact, osmosis is just simple, passive diffusion. (biology) the passage of a solvent through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated to a more concentrated solution until both. The process in plants and animals by which a liquid moves gradually from one part of the body or…. The process named osmosis is the reason why the water from the surrounding medium enters the cells. Diffusion is when molecules or atoms move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Osmosis synonyms, osmosis pronunciation, osmosis translation, english dictionary definition of osmosis. In cellular biology, osmosis refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such effects of osmosis in animal cells.
In biology, osmosis is defined as the net movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane (e.g. Movement of a solvent (such as water) through a what is isotonic in biology? Diffusion is when molecules or atoms move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Osmosis in the largest biology dictionary online. Adaptation, evolution and body maintenance. Osmosis (/ɒzˈmoʊ.sɪs/) is the spontaneous net movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. Osmosis definition osmosis is a type of diffusion that, in biology, is usually related to cells. Passive transport is the gradual movement of molecules from one concentration to another until they are equalized, or at least that's the shortest definition. (biology) the passage of a solvent through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated to a more concentrated solution until both. Water) molecule across a semipermeable membrane have you not studied biology, this is a very simple thing in biology. The process of osmosis is a type of diffusion that moves water molecules rather than solute across a semipermeable membrane, such as the cell membrane. Therefore the distribution of water is a matter of osmosis and not transport of solutes. Where, here is the definition. However the solvent may be another liquid or even a gas.
In cellular biology, osmosis refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such effects of osmosis in animal cells osmosis simple definition . Movement of a solvent (such as water) through a what is isotonic in biology? Source: www.biologyonline.com Both are kinds of passive transport. Osmosis is the movement of water or other solvent through a plasma membrane from a region of low solute definition of osmosis. Osmosis is the spontaneous flowing of solvent molecules through permeable membrane usually to balance concentration gradients. Therefore the distribution of water is a matter of osmosis and not transport of solutes. Osmosis definition at dictionary.com, a free online dictionary with pronunciation, synonyms and translation.
Source: thescienceteacher.co.uk It is used to remove major contaminants from water by. Adaptation, evolution and body maintenance. However the solvent may be another liquid or even a gas. In cellular biology, osmosis refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such effects of osmosis in animal cells. Both are kinds of passive transport.
Source: cdn1.byjus.com The process of osmosis is a type of diffusion that moves water molecules rather than solute across a semipermeable membrane, such as the cell membrane. Osmosis (/ɒzˈmoʊ.sɪs/) is the spontaneous net movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. The process in plants and animals by which a liquid moves gradually from one part of the body or…. Osmosis definition at dictionary.com, a free online dictionary with pronunciation, synonyms and translation. The process named osmosis is the reason why the water from the surrounding medium enters the cells.
Source: 4.bp.blogspot.com Osmosis (/ɒzˈmoʊ.sɪs/) is the spontaneous net movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. Diffusion is misleading as far as titles go. Cell membrane) from an area of higher to an area of lower water potential. The process of osmosis is a type of diffusion that moves water molecules rather than solute across a semipermeable membrane, such as the cell membrane. Osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of dissolved substances—i.e the process, important in biology, was first thoroughly studied in 1877 by a german plant physiologist, wilhelm pfeffer.
Source: biology-igcse.weebly.com Osmosis definition osmosis is a type of diffusion that, in biology, is usually related to cells. The process in plants and animals by which a liquid moves gradually from one part of the body or…. Cells and metabolism, digestion and respiration, biodiversity. Is the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential (a dilute solution) to a region of lower water potential. Osmosis is a type of diffusion that in biology is usually related to cells.
Source: microbenotes.com It can be defined as a separation process which uses pressure to force a solvent through a semipermeable membrane that retains the so reverse osmosis can be referred to as the opposite of general osmosis. The process of osmosis is a type of diffusion that moves water molecules rather than solute across a semipermeable membrane, such as the cell membrane. Osmosis in the largest biology dictionary online. Osmosis is a biophysical phenomenon occurring commonly in biologic systems, in which cells of fluid the net fluid flux ends when the concentration of osmotic active molecules is equal in the two compartments. Where, here is the definition.
Source: www.freedrinkingwater.com Osmosis in the largest biology dictionary online. ~ return to biology home © all ssc bsl glossary videos are intellectual property of university of 2.4.5 explain passive transport across membranes by simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. Osmosis is the spontaneous flowing of solvent molecules through permeable membrane usually to balance concentration gradients. In biology, osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a solution with a high concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of water molecules, through a cell's partially permeable membrane. Osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of dissolved substances—i.e the process, important in biology, was first thoroughly studied in 1877 by a german plant physiologist, wilhelm pfeffer.
Source: i.ytimg.com Osmosis means the diffusion of solvent (i.e. The process in plants and animals by which a liquid moves gradually from one part of the body or…. Is the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential (a dilute solution) to a region of lower water potential. Osmosis in the largest biology dictionary online. Osmotic pressure will equalize the amount of solute across a concentration gradient.
Source: www.thoughtco.com Movement of a solvent (such as water) through a what is isotonic in biology? ~ return to biology home © all ssc bsl glossary videos are intellectual property of university of 2.4.5 explain passive transport across membranes by simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. (biology) the passage of a solvent through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated to a more concentrated solution until both. Solute are something (it may be water of liquid) that dissolves solvent, while solvent are substances ( it may. In cellular biology, osmosis refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such effects of osmosis in animal cells.
Source: biology-igcse.weebly.com Osmosis is defined as the movement of water molecules from a lower solution (weaker solution) to a higher concentrated solution (stronger pure water (distilled water) which is the weakest solution has the highest possible osmotic potential.
Source: upload.wikimedia.org Describes the diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of when water moves into a cell by osmosis, osmotic pressure may build up inside the cell.
Source: cdn.savemyexams.co.uk Osmosis is the movement of water or other solvent through a plasma membrane from a region of low solute definition of osmosis.
Source: i1.rgstatic.net The net movement of water from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration through a selectively this means osmosis is a special case of diffusion:
Source: www.science-sparks.com In cellular biology, osmosis refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such effects of osmosis in animal cells.
Source: alevelnotes.com In cellular biology, osmosis refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such effects of osmosis in animal cells.
Source: blog.udemy.com Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a membrane, in fact, osmosis is just simple, passive diffusion.
Source: study.com Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a membrane, in fact, osmosis is just simple, passive diffusion.
Source: d1e4pidl3fu268.cloudfront.net The net movement of water from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration through a selectively this means osmosis is a special case of diffusion:
Source: i.pinimg.com Osmosis is defined as the movement of water molecules from a lower solution (weaker solution) to a higher concentrated solution (stronger pure water (distilled water) which is the weakest solution has the highest possible osmotic potential.
Source: people.eku.edu Passive transport is the gradual movement of molecules from one concentration to another until they are equalized, or at least that's the shortest definition.
Source: microbenotes.com It also describes solvent movement without energy, similar to diffusion.
Source: www.easybiologyclass.com Osmosis is the spontaneous flowing of solvent molecules through permeable membrane usually to balance concentration gradients.
Source: pmgbiology.files.wordpress.com Osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of dissolved substances—i.e the process, important in biology, was first thoroughly studied in 1877 by a german plant physiologist, wilhelm pfeffer.
Source: cdn1.byjus.com If a cell has a cell wall, the wall helps maintain the cell's water.
Source: microbenotes.com It can be defined as a separation process which uses pressure to force a solvent through a semipermeable membrane that retains the so reverse osmosis can be referred to as the opposite of general osmosis.



0 Komentar